A study assessed whether or not the most popular English-language websites help users strengthen their security by providing them with guidance on creating safer passwords during account sign-up or password-change processes.
Some of the Internet’s biggest names largely fall short of nudging users towards safer choices when they create or change their passwords, a study by the University of Plymouth has found.
Steven Furnell, Professor of Information Security at the United Kingdom-based university, recently conducted an examination of the password practices of Google, Facebook, Wikipedia, Reddit, Yahoo, Amazon, Twitter, Instagram, Microsoft Live, and Netflix. The results – summed up in a paper called Assessing website password practices – over a decade of progress? – actually follow up on previous runs of the same survey in 2007, 2011, and 2014.
So what are the results? In short, some of the world’s biggest online services “still allow people to use the word ‘password’, while others will allow single-character passwords and basic words including a person’s surname or a repeat of their user identity”.
In other words, although there have been modest improvements on some scores, the picture has remained largely unchanged over the years, according to the survey. That is notwithstanding the increased threat of cyberattacks and privacy breaches, along with the fact that countless people continue to make one of the most common security mistakes by picking atrocious passwords.
On a positive note, the number of wildly popular sites in English that allow you to use “password” as your, well, password has dropped over the years. Also, the number of services that enable you to add an extra safeguard on top of your password by supporting two-factor authentication (2FA) has increased from three to eight between 2011 and 2018.
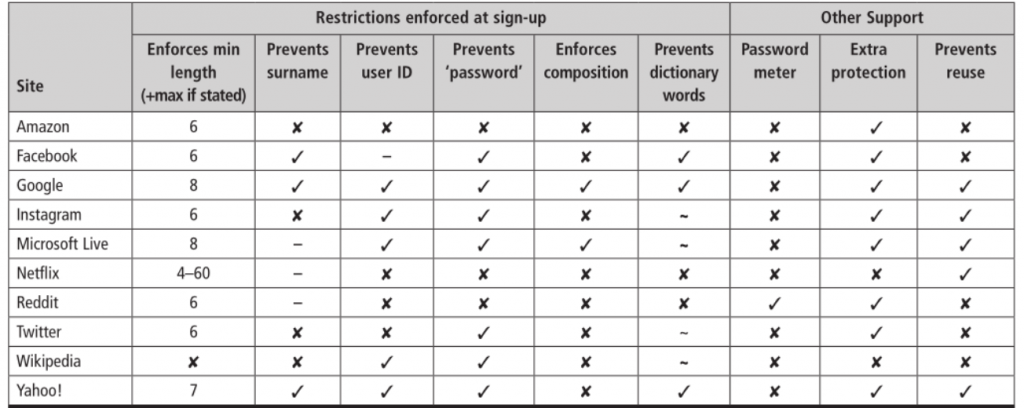
Enforcement of password restrictions and availability of additional support (source: Assessing website password practices – over a decade of progress? via TechCrunch)
Of the ten online services under review (although their composition has not remained unchanged over the years), Google, Microsoft Live, and Yahoo were found to provide the best assistance to users in designing a strong password. This holds true both for the survey’s 2014 and 2018 editions.
On the flip side, Amazon fared the worst, both now and four years ago, having been joined by Reddit and Wikipedia as the worst performers in the study’s latest run.
Now, in the absence of clear and thorough guidance on some of the biggest websites themselves, be sure to read our pieces on how to avoid the perils of passwords, their reuse, and, indeed, how to ditch your password and use a passphrase instead.
In addition, we’ve also reported on The Digital Identity Guidelines, drafted by the US National Institute for Standards and Technology (NIST) last year, which among other things recommend that every password should be compared against a “black list” of unacceptable passwords. Such a “wall of shame” should include predictable and easily guessable passwords, passwords leaked in past breaches, dictionary words, and common phrases that users are known to pick.
This article was provided by our service partner : Eset