The next version of windows server is here and its packed with a lineup of great new features. From software-defined storage, network improvements and Docker-driven containers.
True to type with the new version of Windows Server 2016, we are presented with a multitude of new features. Added networking and storage capabilities build on the software defined infrastructure which began its initiation in Windows Server 2012. Microsoft’s focus on the cloud is apparent with capabilities such as containers and Nano Server. Security is still priority with the shielded VMs features.
Docker- Driven Containers
Microsoft has worked together with Docker to bring full support for the Docker ecosystem to Windows Server 2016. Docker containers wrap a piece of software in a complete filesystem that contains everything needed to run: code, runtime, system tools, system libraries – anything that can be installed on a server. This guarantees that the software will always run the same, regardless of its environment. Containers represent a huge step for Microsoft as it embraces the open source world. You install support for Containers using the standard method to enable Windows features through Control Panel or via the PowerShell command:
Install-WindowsFeature containers
You must also download and install the Docker engine to get all of the Docker utilities. This line of PowerShell will download a Zip file with everything you need to install Docker on Windows Server 2016:
Invoke-WebRequest “https://get.docker.com/builds/Windows/x86_64/docker-1.12.1.zip” -OutFile “$env:TEMP\docker-1.12.1.zip” -UseBasicParsing
Full documentation for getting started with containers can be found on the Microsoft MSDN website. New PowerShell cmdlets provide an alternative to Docker commands to manage your containers (see Figure 1).
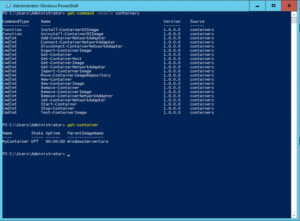
Figure 1: You can manage both Windows Server Containers and Hyper-V Containers through native Docker commands or through PowerShell (shown).
It’s important to note that Microsoft supports two different container models: Windows Server Containers and Hyper-V Containers. Windows Server Containers are based on the typical Docker concepts, running each container as an application on top of the host OS. On an opposite note, Hyper-V Containers are completely isolated virtual machines, incorporating their own copy of the Windows kernel, but more lightweight than traditional VMs.
Windows containers are built against a specific operating system and are crosscomplied with Linux to provide the same experience and common Docker engine. For you, this means that Windows containers supports the Docker experience including the Docker command structure, Docker repositories, Docker datacenter and Orchestration. In addition, Windows containers extends the Docker Community to provide Windows innovations such as PowerShell to manage Windows or Linux containers.
Nano Server
Nano Server is another key component of Microsoft’s strategy to be highly competitive in the private cloud market. Nano Server is stripped-down version of Windows Server 2016. It’s so stripped down, in fact, that it doesn’t have any direct user interface besides the new Emergency Management console. You will manage your Nano instances remotely using either Windows PowerShell or the new Remote Server Administration Tools. The first benefit is Infrastructure host, that can runs Hyper-V, File Server, Failover Clustering and it will be a great container host as well.
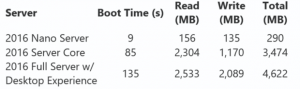
Figure 2: Nano Server not only boots faster, it consumes less memory and less disk than any other version of Windows Server.
Storage Qos Updates
Storage QoS enables administrators to provide virtual machines, and their applications by extension, predictable performance to an organization’s networked storage resources. Storage QoS helps level the playing field while virtual machines jockey for storage resources. According to a related Microsoft support document, the feature helps reduce “noisy neighbor” issues caused by resource-intensive virtual machines. “By default, Storage QoS ensures that a single virtual machine cannot consume all storage resources and starve other virtual machines of storage bandwidth,” stated the company.
It also offers administrators the confidence to load up on virtual machines by providing better visibility into their virtual machine storage setups. “Storage QoS policies define performance minimums and maximums for virtual machines and ensures that they are met. This provides consistent performance to virtual machines, even in dense and overprovisioned environments,” Microsoft wrote.
Windows Server 2016 allows you to centrally manage Storage QoS policies for groups of virtual machines and enforce those policies at the cluster level. This could come into play in the case where multiple VMs make up a service and should be managed together. PowerShell cmdlets have been added in support of these new features, including Get-StorageQosFlow, which provides a number of options to monitor the performance related to Storage QoS; Get-StorageQosPolicy, which will retrieve the current policy settings; and New-StorageQosPolicy, which creates a new policy.
Shielded VMs
Shielded VMs, or Shielded Virtual Machines, are a security feature introduced in Windows Server 2016 for protecting Hyper-V Generation 2 virtual machines (VMs) from unauthorized access or manipulating. Shielded VMs use a centralized certificate store and VHD encryption to authorize the activation of a VM when it matches an entry on a list of permitted and verified images. VMs use a virtual TPM to enable the use of disk encryption with BitLocker. Live migrations and VM-state are also encrypted to prevent man-in-the-middle attacks.
The HGS – Host Guardian Service (HGS) (typically, a cluster of 3 nodes) supports two different attestation modes for a guarded fabric:
TPM-trusted attestation (Hardware based)
Admin-trusted attestation (AD based)
TPM-trusted attestation is recommended because it offers stronger assurances, as explained in the following table, but it requires that your Hyper-V hosts have TPM 2.0. If you currently do not have TPM 2.0, you can use Admin-trusted attestation. If you decide to move to TPM-trusted attestation when you acquire new hardware, you can switch the attestation mode on the Host Guardian Service with little or no interruption to your fabric.
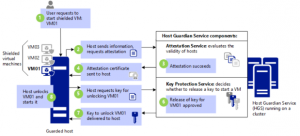
Figure 3: Shielded VMs are encrypted at rest using BitLocker. They can be run by an authorized administrator only on known, secure, and healthy hosts.
Fast Hyper-V Storage with ReFS
The Resilient File System (ReFS) is another feature introduced with Windows Server 2012. ReFS has huge performance implications for Hyper-V. New virtual machines with a fixed-size VHDX are created instantly. The same advantages apply to creating checkpoint files and to merging VHDX files created when you make a backup. These capabilities resemble what Offload Data Transfers (ODX) can do on larger storage appliances.
RemoteFX
Microsoft also did some improvements on Windows Server 2016 RemoteFX which now includes support for OpenGL 4.4 and OpenCL 1.1 API. It also allows you to use larger dedicated VRAM and VRAM in now finally configurable.
Hyper-V rolling upgrades
Windows Server 2016 enables you to upgrade to a new operating system without taking down the cluster or migrating to new hardware. In previous versions of Windows Server, it was not possible to upgrade a cluster without downtime, this caused significant issues for production systems. This new process is is similar in that individual nodes in the cluster must have all active roles moved to another node in order to upgrade the host operating system. The difference is that all members of the cluster will continue to operate at the Windows Server 2012 R2 functional level (and support migrations between old and upgraded hosts) until all hosts are running the new operating system and you explicitly upgrade the cluster functional level (by issuing a PowerShell command).
Hyper-V hot add NICs and memory
Previous versions of Hyper-V did not allow you to add a network interface or more memory to a running virtual machine. Microsoft now allows you to make some critical machine configuration changes without taking the virtual machine offline. The two most important changes involve networking and memory.
In the Windows Server 2016 version of Hyper-V Manager, you’ll find that the Network Adapter entry in the Add Hardware dialog is no longer grayed out. The benefit is that an administrator may now add network adapters and memory to VMs originally configured with fixed amounts of memory, while the VM is running.
Storage Replica
Storage Replica is a new feature that enables storage-agnostic, block-level, synchronous replication between clusters or servers for disaster preparedness and recovery, as well as stretching of a failover cluster across sites for high availability. Synchronous replication enables mi Storage Space Direct (S2D), formally known as “Shared Nothing”.WS2016 introduces the second iteration of the software-defined storage feature known as Storage Spaces to bring cloud inspired capabilities to the data center with advances in computing, networking, storage, and security. This S2D local storage architecture takes each storage node and pools it together using Storage Spaces for data protection (two- or three-way mirroring as well as parity). The local storage can be SAS or SATA (SATA SSDs provide a significant cost savings) or NVMe for increased performance.
Enabling this feature can be accomplished with a single PowerShell command:
Enable-ClusterStorageSpacesDirect
This command will initiate a process that claims all available disk space on each node in the cluster, then enables caching, tiering, resiliency, and erasure coding across columns for one shared storage pool.
storing of data in physical sites with crash-consistent volumes, ensuring zero data loss at the file system level. Asynchronous replication allows site extension beyond metropolitan ranges.
Networking enhancements
Converged Network Interface Card (NIC). The converged NIC allows you to use a single network adapter for management, Remote Direct Memory Access (RDMA)-enabled storage, and tenant traffic. This reduces the capital expenditures that are associated with each server in your datacenter, because you need fewer network adapters to manage different types of traffic per server.
Another facility is Packet Direct. Packet Direct provides a high network traffic throughput and low-latency packet processing infrastructure.
Windows Server 2016 includes a new server role called Network Controller, which provides a central point for monitoring and managing network infrastructure and services. Other enhancements supporting the software-defined network capabilities include an L4 load balancer, enhanced gateways for connecting to Azure and other remote sites, and a converged network fabric supporting both RDMA and tenant traffic.
As we move to virtualized instances in the cloud, it becomes important to reduce the footprint of each instance, to increase the security around them, and to bring more automation to the mix. In Windows Server 2016, Microsoft is pushing ahead on all of these fronts at once. Windows Server 2016 makes it easier to pick up the cloud way of functioning so you can change the way your server apps work as quickly as you want, even if you’re not using the cloud.