Many CIOs are now adopting a cloud-first strategy and backing up and recovering critical data in the cloud is on the rise. If you don’t have a permanent CIO to manage your IT department, consider hiring an interim CIO. As more and more companies explore the idea of migrating applications and data to the cloud, questions like “How secure are cloud services?” arise. While there isn’t a standout number one concern when it comes to cloud computing, the one thing we can be sure about is that security is front and center in CIO’s minds. Veeam has identified the top two concerns from our recent 2016 customer survey to be security and price. See the graph of responses below:
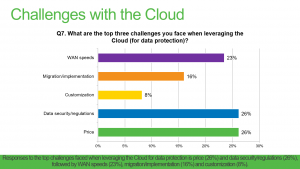
Quite inevitably, cloud has come with new challenges and we’ll be exploring them all in this cloud challenges blog series. It has also come with some genuine security risks but as we will uncover, cloud backup security has more to do with your implementation of it to successfully ensure data security when moving to the cloud. With cloud, security has to be top priority. The benefits of flexibility and scalability you get from the cloud should not mean sacrificing any security at all.
What are the most important cloud backup security risks?
Stolen authentication/credentials
Attacks on data happen more often than not due to weak password usage, or poor key and certificate management. Issues tend to happen as multiple allocations and permission levels begin to circulate and this is where good credential management systems and practices can really help.
One-time generated passwords, phone-based authentication and other multifactor authentication systems make it difficult for attackers wanting to gain access to protected data because they need more than just one credential in order to log in.
Data breaches
Data breaches can be disastrous for organizations. Not only have they violated the trust of their customers by allowing data to be leaked, but it also opens them up to facing fines, lawsuits and even criminal indictments. The brand tarnishing and loss of business from such an event can leave a business with a long road to recovery at best.
Despite the fact that cloud service providers typically do offer security methods to protect tenants’ environments, ultimately you – the IT professional – are responsible for protection of your organization’s data. In order to protect even the idea of a breach, you need to become a fan of encryption. If you use cloud for storage, experts agree data should be encrypted at no less than 256-bit AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) before it leaves your network. The data should be encrypted a second time while in transit to the cloud and a third time while at rest stored in the cloud. It is important to do your research and enquire into the encryption used by the application, and by the service provider when the data is at rest in order to ensure safe and secure cloud backups.
Lack of due diligence
A key reason moving data to the cloud fails, becomes vulnerable or worse becomes subject to an attack or loss is due to poor planning and implementation. To successfully implement a cloud backup or disaster recovery strategy, careful and deliberate planning should take place. This should first involve considering and understanding all of the risks, vulnerabilities and potential threats that exist. Secondly, an understanding of what countermeasures need to be taken in order to ensure secure restore or recovery of backups and replication, such as ensuring your network is secure or access to key infrastructure is restricted. Due diligence in approaching the cloud should also involve an alignment of your IT staff, the service provider and the technologies and environment being leveraged. The service provider must be seamlessly integrated with the cloud backup and recovery software you plan to utilize for optimal security and performance of your virtualized environment.
Multi-tenant environment
Service providers offer cost-effectiveness and operations efficiencies by providing their customers with the option of shared resources. In choosing a service that is shared, it’s essential that the risks are understood. Ensuring that each tenant is completely isolated from other tenant environments is key to a multi-tenant platform. Multi-tenant platforms should have segregated networks, only allow privileged access and have multiple layers of security in the compute and networking stacks.
Service provider trust and reliability
The idea of moving data offsite into a multi-tenant environment where a third party manages the infrastructure can give even the boldest IT professionals some anxiety. This comes with the perceived lack of control they might have on cloud backup security. To combat this, it is essential to choose a service provider you trust who is able to ease any security doubts. There are a variety of compliance standards a provider can obtain, such as ISO9001 or SOC 2 & SSAE 16 and it’s important to take note of these as you search for a provider. In addition to standards, look for a service provider that has a proven track record of reliability – there are plenty of online tools that report on provider network uptime. Physical control of the virtual environment is also paramount. You must seek a secure data center, ideally with on-site 24/7 security and mantraps with multi-layered access authentication.
So, is the cloud secure?
Yes, the cloud is secure but only as secure as you make it. From the planning and the processes in place, to the underlying technology and capabilities of your cloud backup and recovery service. All these elements combined can determine your success. It is up to you to work with your choice of service provider to ensure the security of your data when moving to cloud backups or DRaaS. Another critical aspect is partnering with a data management company experienced in securely shifting and storing protected data in the cloud.
Veeam and security
We provide flexibility in how, when and where you secure your data for maximum security matched with performance. With AES 256-bit encryption, you have the ability to secure your data at all times: During a backup, before it leaves your network perimeter, during movement between components (e.g., proxy to repository traffic), for when data must stay unencrypted at the target and while your backup data is at rest in its final destination (e.g., disc, tape or cloud). It is also perfect for sending encrypted backups off site using Backup Copy jobs with WAN Acceleration.
You have a choice over when and where you encrypt backups. For example, you can leave local Veeam backups unencrypted for faster backup and restore performance, but encrypt backups that are copied to an offsite target, tape or the cloud. You can also protect different backups with different passwords, while actual encryption keys are generated randomly within each session for added backup encryption security.
Here are some links with more details on encryption and related information:
This article was provided by our service partner Veeam
Migrating to the cloud backups
We have already talked about how secure backups can be in a cloud environment and what the cost may be of not leveraging the potential of DRaaS. The next step would be to start thinking about how to migrate your infrastructure or backups/replicas to cloud backups and at what scale it has to be done. We will review the main points that you need to consider and check prior to initiating your move into the world of cloud.
Who can benefit from the cloud?
The short answer is a bold one: Everyone. Regardless of the size of the operation, there is a good incentive in road mapping your migration over to the cloud as it brings a whole new level of accessibility, scalability and long-term cost savings. But what does that really mean?
When it comes to conventional disaster recovery sites, it’s hard to plan everything beforehand because you have no way of knowing when the disaster is going to strike and at what scale. You’re only as flexible as the hardware that you’re provided with. Any additional capacity would require time and more money to acquire and install.
That’s where the cloud steps up the game. You are presented with a variety of options that allow you to build a flexible DR environment with the ability to grow and shrink its capacity at will. The only price you’ll pay is for the actual hardware in use, thus granting an incredible scalability that is ready for any DR needs. Not every provider possesses such ability at a full scale, but there’s plenty of options to pick from based on your particular needs.
The two approaches Veeam has for businesses with on-premises deployments wanting to get backups or replicas to the cloud are Backup as a Service (BaaS) and Disaster Recovery as a Service (DRaaS). These approaches utilize cloud and service provider technologies which are flexible enough for any use case and you can avoid the cost and complexity of building and maintaining an offsite infrastructure.
So, how hard is it to migrate to the cloud?
What’s important to remember is that migrating data to the cloud is not a one-day feat and is a project that will require planning and a timeline. However, depending on what data management software you use, getting data offsite to the cloud can be a very simplified experience.
Migrating to the cloud certainly doesn’t require you to drop all the investments in your existing DR infrastructure, should you have one. If you’re already running an on-premises infrastructure, then you know that any hardware has its lifecycle and will eventually be replaced. So, you can plan to move your servers and applications to the cloud environment as the time for hardware renewals shows up on the calendar.
If you’re just starting off at the stage of designing your infrastructure then it would be even more beneficial, as you are getting high-class disaster-proof hardware used on Enterprise levels of operation at an affordable price and right-away at your disposal. No need to worry about building and maintaining your own DR site, all the more so about the time to set everything up from scratch.
In any case scenario, Veeam® has the tools to make your migration to the cloud as easy as your daily backup tasks. In fact, even though Veeam Cloud Connect Backup and Replication are used for archival purposes and providing continuous synchronization, they’re a perfect instrument for migrating your infrastructure to the cloud without any hassle.
What should be migrated first?
The first contenders are the servers that will fully benefit from the flexibility and added performance of the cloud. But, not every server or application needs to or can be migrated right away. You need to plan it in the way that won’t obstruct your production performance more than usual hardware migration or upgrade. It’s important to make sure the migration to the cloud won’t cause you trouble during the process or after the completion. That can be done by testing the performance of servers or applications in the lab to find out about any hiccups beforehand. Sometimes an existing set of dependencies, like an on-site SQL database or Active Directory, can make it harder to simply move some applications without correcting their workflow.
In such scenarios the use of hybrid cloud might be helpful. In a hybrid setup one part of your cloud infrastructure is private and running under your full control on-premises and the other part is in public cloud, making use of all the servers that are easily moved to cloud or will benefit from it the most.
Where do you start?
No matter the size of the infrastructure, Veeam Cloud Connect offers a solution to fully control and easily migrate on premises data to highest standard cloud environments – requiring no network (VPN) setup or change to the customer environment. And whether you plan on implementing a big bang migration strategy or the trickle migration strategy, Veeam Cloud Connect allows for both methods.
_________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
This article was provided by our service partner Veeam
Intel igb/e1000 driver showing dropped packets on the interface
Recently I ran into a strange issue where the Intel NIC was showing dropped packets on the interface. This particular server was having other issues (performance-ish type) so we were eager to get to the bottom of this.
Symptoms and interesting finds…
A solution, though not perfect was finally discovered. Disable BPDU/STP on the switch. The environment only had one switch so it wasn’t huge issue. On the Cisco the command was:
Some interesting resources on this:
https://forums.suse.com/showthread.php?1320-Mystery-RX-packet-drops-on-SLES11-SP2-every-30-sec
6 Steps to Client Onboarding Success
Client onboarding is the first time new clients get to see how you operate. It’s when first impressions are formed; impressions that could have a lasting impact. And if you don’t deliver on promises that were made during the sales process, what impression do you think they’ll be left with?
To make sure your client relationship starts off on the right foot (sorry lefties), you just need to follow a few simple steps.
1. Have a Plan
I’m always surprised to learn just how many people fail to use a project plan. I can’t stress this enough; a templated project plan is key to transforming your client onboarding process from mass chaos to a seamless, automated process. Outline every step that has to take place from the date the contract is signed to service go-live.
2. Use Time-Saving Automation
Using an IT automation platform, such as ConnectWise Automate (formerly LabTech), can cut hours off of the manual engineering tasks many of us still do today. Let’s look at some of the places you can shave a few hours from the client onboarding process.
3. Optimize and Secure Endpoints
Automate detects more than 40 different antivirus (AV) vendors, so let it handle the AV rip and replace process. As part of the security rollout, you’ll also want to deploy a second opinion scanner, such as HitmanPro, to automatically scan for and remediate any security issues your AV software might miss. Follow that up by deploying desktop optimization software, such as CCleaner, to get those systems running smoothly without a technician ever having to touch a single desktop.
4. Software Deployment
You’ll need to make sure common applications, such as Adobe and Java, are installed and updated. You can automate this task. Using some simple logic, the Automate script engine can easily search for missing or outdated software and then install or update accordingly. No more combing through reports or visiting each desktop to find out what’s there and what’s not.
5. Policy Deployment
Missing a critical error at any stage of the game can be detrimental; missing it during onboarding is simply unacceptable. Automate intuitively detects a machine’s role, determines which policies should be applied and automatically applies the right ones. Never again get that awkward phone call from your new client asking why their email isn’t working, and you didn’t know about it because someone forgot to apply a monitor template.
6. Educate Your Sales Team
After your project plan is in place and your automated processes are built, it’s time to educate your sales team. Let them see how the onboarding process works and how long it really takes, so they can set realistic expectations from the start.
8 Essential Steps to Implement IT Best Practices
In the past, we’ve defined best practices and looked at how they benefit your business. Now let’s talk about how to implement best practices so you’ll start seeing results.
Implementing best practices is just like any other project you take on. Success comes from accounting for every detail. Make sure you have these 8 things covered when implementing best practices in your IT business:
Growing your business with best practices means happier customers, more productive employees and a better bottom line. Use these 8 tips to streamline best practice implementation, so you’ll see results fast.
Top 5 Best Practices for your Help Desk
A Help Desk is designed to be the first point of contact for customers when they have requests or problems with their technology services. And you, as the technology service provider are responsible for addressing those issues as quickly and efficiently as possible. It is essential, then, to ensure a strategic method of managing this single point of contact for requests and issues. This will include tracking inbound and outbound ticket processes, escalation procedures, and ticket resolution.
Good luck finding clients that are ok with issues slipping through the cracks and hanging out there for extended periods of time. People just won’t stand for it, so to ensure this doesn’t happen, check out our Top 5 Best Practices for your Help Desk.
Everything is a Ticket – All incidents and requests must be a ticket to properly capture all work performed, regardless of length, nature, or severity of the request.
Keep Customers in the Loop – Leverage Closed Loop to communicate with the customers. You should be updating them on progress and the status of their service requests.
All Roads Lead to Rome – Rome being your service boards, everything ends up as a service ticket on your service boards regardless of the source. The service board is what then controls your next step through workflows.
My Life is My Service Board – Help Desk employees work service tickets on their assigned service boards in order of assignment and the service level agreement’s priority, urgency, and impact.
All Time, All of the Time, On Time – All employees must enter all time worked, on everything they work (all of the time), as it happens (on time).
Microsoft enhances troubleshooting support for Office365
There’s a new tool from Microsoft for Office365 that scans files for headache-inducing problems in OneDrive for Business
It appears that last week Microsoft added a new and largely unheralded capability to the Office 365 checker tool.
A change to Microsoft’s main troubleshooting article for OneDrive for Business, KB 3125202, added a reference to an option in the Microsoft Support and Recovery Assistant for Office 365 tool that can be used to scan for files that are too big, file and folder names that have invalid characters, for path names that exceed the length limit, and several other headache-inducing problems. This appears to be a new capability for the Office 365 checker tool.
Here’s what the new information says:
This looks like an excellent tool for anyone troubleshooting OneDrive for Business problems.
This is a repost from InfoWorld
Microsoft to revamp its documentation for security patches
Microsoft has eliminated individual patches from every Windows version, and Security Bulletins will go away soon, replaced by a spreadsheet with tools
With the old method of patching now completely gone—October’s releases eliminated individual patches from every Windows version—Microsoft has announced that the documentation to accompany those patches is in for a significant change. Most notable, Security Bulletins will disappear, replaced by a lengthy list of patches and tools for slicing and dicing those lists.
Security Bulletins go back to June 1998, when Microsoft first released MS98-001. That and all subsequent bulletins referred to specific patches described in Knowledge Base articles. The KB articles, in turn, have detailed descriptions of the patches and lists of files changed by each patch. The Security Bulletins serve as an overview of all the KB patches associated with a specific security problem. Some Security Bulletins list dozens of KB patches, each for a specific version of Windows.
Starting in January, we’ll have two lists—or, more accurately, two ways of viewing a master table.
Keep in mind that we’re only talking about security patches and the security part of the Windows 10 cumulative updates. Nonsecurity patches and Win7/8.1 monthly rollups are outside of this discussion.
To see where this is going and to understand why it’s vastly superior to the Security Bulletin approach, look at the lists for November 8, this month’s Patch Tuesday. The main Windows Update list
shows page after page of security bulletins, identified by MS16-xxx numbers, and those numbers have become ambiguous. See, for example, MS16-142 on that list, which covers both the Security-only update for Win7, KB 3197867, and the Monthly rollup for Win7, KB 3197868. The MS16-142 Security Bulletin itself runs on for many pages.
Now flip over to the Security Updates Guide. In the filter box type
windows 7and press Enter. You see four security patches (screenshot below): IE11 and Windows, both 32- and 64-bit. They’re all associated with KB 3197867.In the Software Update Summary, searching for “windows 7” yields only one entry, for the applicable KB number (screenshot below).
Here’s why the tools are important. On this month’s Patch Tuesday, we received 14 Security Bulletins. Those Security Bulletins actually contain 55 different patches for different KB numbers; the Security Bulletin artifice groups those patches together in various ways. The 55 different security patches actually contain 175 separate fixes, when you break them out by the intended platform.
There’s a whole lotta patchin’ goin’ on.
Starting this month, you can look at the patches either individually (in the Security Updates Guide) or by platform (in the Software Update Summary), or you can plow through those Security Bulletins and try to find the patches that concern you. Starting in January, per the Microsoft Security Response Center, the Security Bulletins are going away.
Of course, the devil’s in the implementation details, but all in all this seems to me like a reasonable response to what has become an untenable situation.
This is a repost from http://www.infoworld.com/
Cloud backup security concerns
Many CIOs are now adopting a cloud-first strategy and backing up and recovering critical data in the cloud is on the rise. If you don’t have a permanent CIO to manage your IT department, consider hiring an interim CIO. As more and more companies explore the idea of migrating applications and data to the cloud, questions like “How secure are cloud services?” arise. While there isn’t a standout number one concern when it comes to cloud computing, the one thing we can be sure about is that security is front and center in CIO’s minds. Veeam has identified the top two concerns from our recent 2016 customer survey to be security and price. See the graph of responses below:
Quite inevitably, cloud has come with new challenges and we’ll be exploring them all in this cloud challenges blog series. It has also come with some genuine security risks but as we will uncover, cloud backup security has more to do with your implementation of it to successfully ensure data security when moving to the cloud. With cloud, security has to be top priority. The benefits of flexibility and scalability you get from the cloud should not mean sacrificing any security at all.
What are the most important cloud backup security risks?
Stolen authentication/credentials
Attacks on data happen more often than not due to weak password usage, or poor key and certificate management. Issues tend to happen as multiple allocations and permission levels begin to circulate and this is where good credential management systems and practices can really help.
One-time generated passwords, phone-based authentication and other multifactor authentication systems make it difficult for attackers wanting to gain access to protected data because they need more than just one credential in order to log in.
Data breaches
Data breaches can be disastrous for organizations. Not only have they violated the trust of their customers by allowing data to be leaked, but it also opens them up to facing fines, lawsuits and even criminal indictments. The brand tarnishing and loss of business from such an event can leave a business with a long road to recovery at best.
Despite the fact that cloud service providers typically do offer security methods to protect tenants’ environments, ultimately you – the IT professional – are responsible for protection of your organization’s data. In order to protect even the idea of a breach, you need to become a fan of encryption. If you use cloud for storage, experts agree data should be encrypted at no less than 256-bit AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) before it leaves your network. The data should be encrypted a second time while in transit to the cloud and a third time while at rest stored in the cloud. It is important to do your research and enquire into the encryption used by the application, and by the service provider when the data is at rest in order to ensure safe and secure cloud backups.
Lack of due diligence
A key reason moving data to the cloud fails, becomes vulnerable or worse becomes subject to an attack or loss is due to poor planning and implementation. To successfully implement a cloud backup or disaster recovery strategy, careful and deliberate planning should take place. This should first involve considering and understanding all of the risks, vulnerabilities and potential threats that exist. Secondly, an understanding of what countermeasures need to be taken in order to ensure secure restore or recovery of backups and replication, such as ensuring your network is secure or access to key infrastructure is restricted. Due diligence in approaching the cloud should also involve an alignment of your IT staff, the service provider and the technologies and environment being leveraged. The service provider must be seamlessly integrated with the cloud backup and recovery software you plan to utilize for optimal security and performance of your virtualized environment.
Multi-tenant environment
Service providers offer cost-effectiveness and operations efficiencies by providing their customers with the option of shared resources. In choosing a service that is shared, it’s essential that the risks are understood. Ensuring that each tenant is completely isolated from other tenant environments is key to a multi-tenant platform. Multi-tenant platforms should have segregated networks, only allow privileged access and have multiple layers of security in the compute and networking stacks.
Service provider trust and reliability
The idea of moving data offsite into a multi-tenant environment where a third party manages the infrastructure can give even the boldest IT professionals some anxiety. This comes with the perceived lack of control they might have on cloud backup security. To combat this, it is essential to choose a service provider you trust who is able to ease any security doubts. There are a variety of compliance standards a provider can obtain, such as ISO9001 or SOC 2 & SSAE 16 and it’s important to take note of these as you search for a provider. In addition to standards, look for a service provider that has a proven track record of reliability – there are plenty of online tools that report on provider network uptime. Physical control of the virtual environment is also paramount. You must seek a secure data center, ideally with on-site 24/7 security and mantraps with multi-layered access authentication.
So, is the cloud secure?
Yes, the cloud is secure but only as secure as you make it. From the planning and the processes in place, to the underlying technology and capabilities of your cloud backup and recovery service. All these elements combined can determine your success. It is up to you to work with your choice of service provider to ensure the security of your data when moving to cloud backups or DRaaS. Another critical aspect is partnering with a data management company experienced in securely shifting and storing protected data in the cloud.
Veeam and security
We provide flexibility in how, when and where you secure your data for maximum security matched with performance. With AES 256-bit encryption, you have the ability to secure your data at all times: During a backup, before it leaves your network perimeter, during movement between components (e.g., proxy to repository traffic), for when data must stay unencrypted at the target and while your backup data is at rest in its final destination (e.g., disc, tape or cloud). It is also perfect for sending encrypted backups off site using Backup Copy jobs with WAN Acceleration.
You have a choice over when and where you encrypt backups. For example, you can leave local Veeam backups unencrypted for faster backup and restore performance, but encrypt backups that are copied to an offsite target, tape or the cloud. You can also protect different backups with different passwords, while actual encryption keys are generated randomly within each session for added backup encryption security.
Here are some links with more details on encryption and related information:
This article was provided by our service partner Veeam
Wireless authentication with usernames and 802.1x
If you’re at all interested in keeping your network and data secure it’s necessary to implement 802.1x. This authentication standard has a few significant benefits over the typical wireless network password used by many companies.
All enterprise network hardware supports 802.1x and NetCal can implement it to keep your network flexible, fast and secure.
5 Must-Have Features of Your Remote Monitoring Services
Remote Monitoring Services Features You Must Have
As a managed service provider (MSP), we have a desire to take your business to the next level. The MSPs that are successful in this endeavor have a key ingredient in common: they are armed with the right tools for growth. The most critical tool for success in this business is a powerful remote monitoring services and management (RMM) solution.
So the question is, what should you be looking for when you purchase an RMM tool, and why are those features important to your business?
The right RMM tool impacts your business success with five key benefits. With a powerful and feature-rich RMM solution in place, you can:
Work on multiple machines at once
Solve issues without interrupting clients
Integrate smoothly into a professional services automation (PSA) tool
Manage everything from one control center.
To better understand why these features are so influential, let’s talk a little more about each of them.
Automate Any IT Process or Task
Imagine being able to determine a potential incident before your client feels the pain and fix it in advance to avoid that negative business impact. Being able to automate any IT process gives you the proactive service model you need to keep your clients happy for the long haul.
Work on Multiple Machines at Once
To solve complex issues, an MSP must be able to work on all the machines that make up a system. If you are attempting to navigate this maze via a series of webpages, it is hard to keep up with progress and makes it easy to miss a critical item during the diagnosis. Having the ability to work on multiple machines at once is paramount to developing your business model and maximizing your returns.
Solve Issues Without Interrupting Clients
One of the biggest challenges that MSPs face is fixing issues without impacting their clients’ ability to work. With the wrong tools in place, the solution can be nearly as disruptive as the issue it’s meant to fix. The right tool must allow a technician to connect behind the scenes, troubleshoot and remediate the problem without impacting the client’s ability to work.
Integrate Smoothly Into a PSA Tool
Two-way integration between your RMM and PSA solutions eliminates bottlenecks and allows data to flow smoothly between the tools. The goal of integration is to enable you to respond more quickly to client needs as well as capture and store historical information that leads to easier root cause analysis.
A solid integration will also increase sales by turning data into actionable items that result in quotes and add-on solutions. The key areas to examine when looking at how a PSA and RMM integrate are:
Capturing billable time
Assigning incidents based on device and technician
Scheduling and automating tasks
Identifying and managing sales opportunities
Managing and reporting on client configuration information
A solid integration into a PSA will create an end-to-end unified solution to help your more effectively run your IT business.
Manage Everything from One Control Center
The control center for your RMM solution should be the cockpit for your service delivery. Having the ability to manage aspects that are directly related to service delivery such as backup and antivirus from the same control center keeps your technicians working within a familiar environment and speeds service delivery. Also, it cuts down on associated training costs by limiting their activities to the things that matter on a day-to-day basis.
Success means equipping your business with the right features and functionality to save your technicians time while increasing your revenue and profit margins. Selecting an RMM solution that solves for these five influential features is the key to getting started down the path to success. What are you waiting for?
This article was provided by our service partner Labtech.